Cleanroom News, Knowledge Base
The Fundamentals of GMP Cleanroom Classifications
The clean air grades and classifications established by GMP dictate the appropriate environment for producing sterile drugs and biological products. Sterile product manufacturing is categorized into four areas – Grade A, B, C, and D – in compliance with GMP guidelines. Understanding the requirements and grades of GMP can be challenging, especially when dealing with regulatory bodies in other countries. Knowing the highlights of cleanroom environments for Grade A, Grade B, Grade C, or Grade D is important.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) were created to ensure sterile pharmaceutical products are safe, pure, and contain the correct ingredients and amounts. These guidelines aim to minimize the risk of contamination from particles, pyrogens, and microorganisms. The current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) regulations cover various aspects of production, including quality control, packaging, personnel, and GMP facility.
What cleanrooms should comply with GMP standards? As noted above, GMP standards are primarily used in medical and pharmaceutical cleanrooms. Any process that involves the production, filling, compounding, or packaging of sterile pharmaceutical products must comply with GMP standards. This includes industries and applications such as medical device manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, biopharmaceutical manufacturing, regenerative medicine, and cell and gene therapy. The manufacturing of sterile products requires strict adherence to established and validated methods for quality assurance. Implementing a Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) throughout the facility is vital to identify critical control points and assess the effectiveness of all controls, including design, procedural, technical, and organizational measures. The CCS should be regularly updated to continuously improve manufacturing and control methods and reduce risks associated with contamination.
Maintaining a cleanroom environment in your GMP facility is critical for positive outcomes. Cleanrooms are used to control contamination rather than entirely remove it. A higher level of cleanliness is required in cases where operations may lead to defects in the final product. While non-sterile pharmaceuticals may not require a cleanroom, sterile drugs must be manufactured in a clean environment. The GMP clean air grades and classifications are used to define the environment for producing sterile medicines and biological products. The tables below illustrate some highlights of cleanroom environments for Grade A, Grade B, Grade C, or Grade D.
Table 1: Maximum permitted airborne particulate concentration during classification
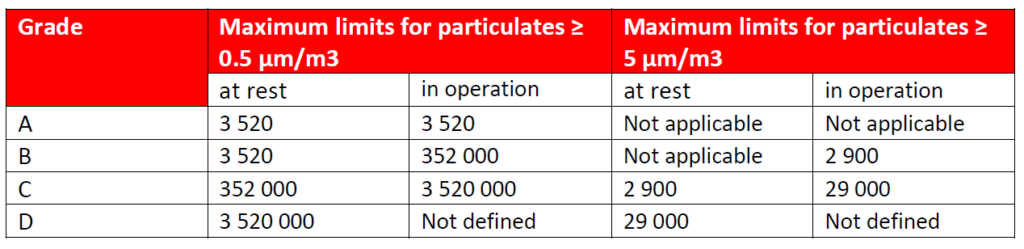
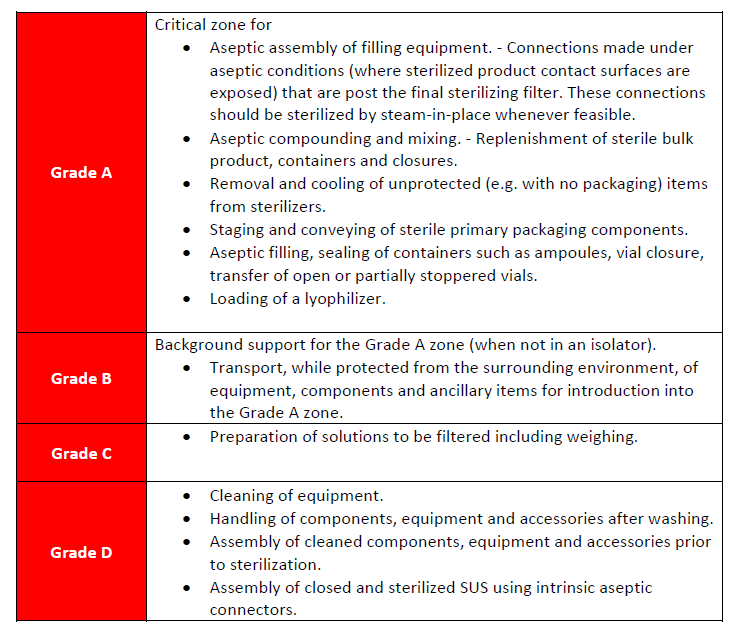
Table 5: Examples of Operations and grades for aseptic preparation and processing operations



















HAVE AN IDEA FOR CONTENT?
We are always looking for ideas and topics to write about.
Contact Us