Berkshire Products, Knowledge Base
What is an ESD Swab?
To understand the purpose of an ESD swab, we first need to grasp what ESD is. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden electric charge transfer between objects with different electrical potentials. This discharge happens when static electricity builds up, often due to friction between two conductive materials. For example, when materials rub against each other, electrons can move from one surface to another. As a result, one material becomes positively charged while the other takes on a negative charge. Examples of electrostatic discharge (ESD) include:
- The static electricity you feel when removing fresh clothes from the dryer.
- Walking across a carpet while wearing socks and then getting shocked by touching a metal object.
- Lightning, we see in the sky.
The significance of ESD increases as electronic devices become smaller and more intricate. Modern microchips and circuits can be extremely sensitive to even the slightest electrical disturbances, making them more vulnerable to damage. A discharge of just a few volts—barely perceptible to the human body—can compromise the integrity of these components, leading to temporary malfunctions or permanent failure.
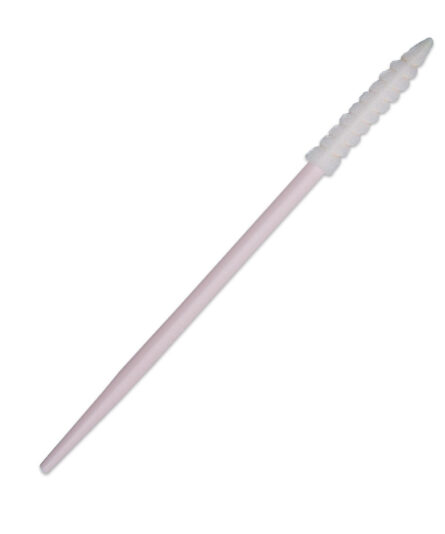
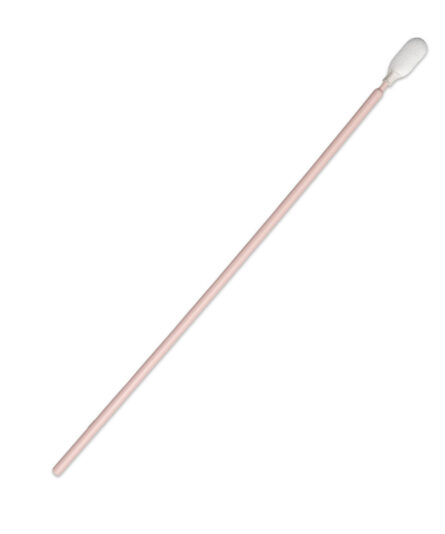
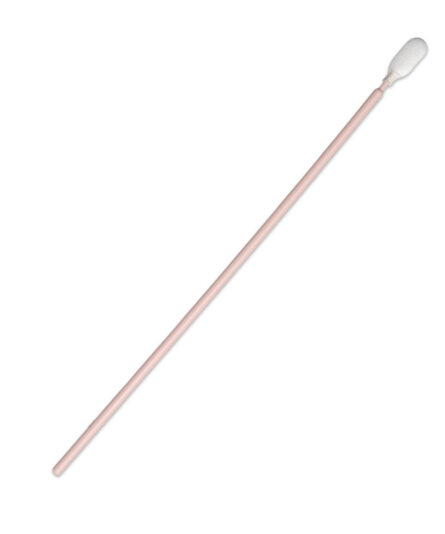
Dissipative swabs are critical in device manufacturing to avoid compromising equipment and components. ESD swabs are specially designed anti-static swabs with dissipative handles to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) and protect sensitive electronics. Key details about ESD swabs include:
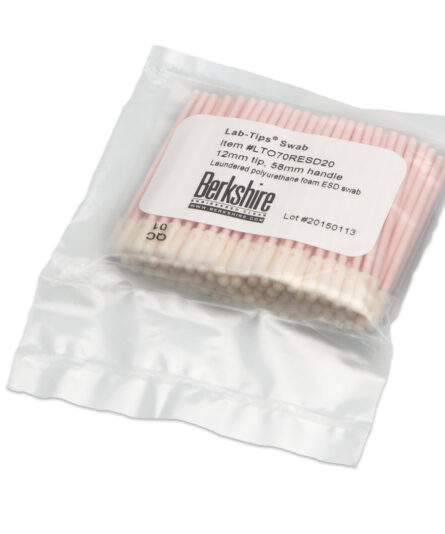
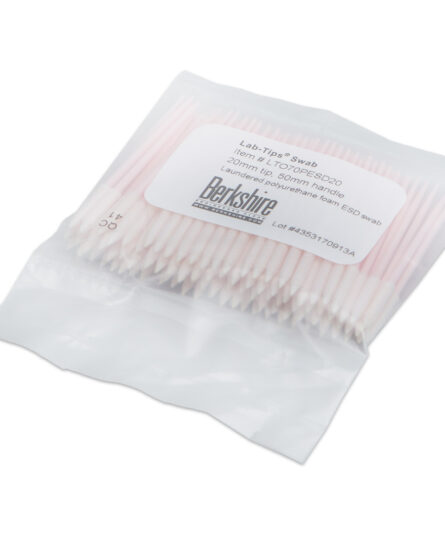
Construction: ESD swabs are made from anti-static materials, including conductive foam, polyester, cotton, or non-woven materials, and they have anti-static or dissipative handles.
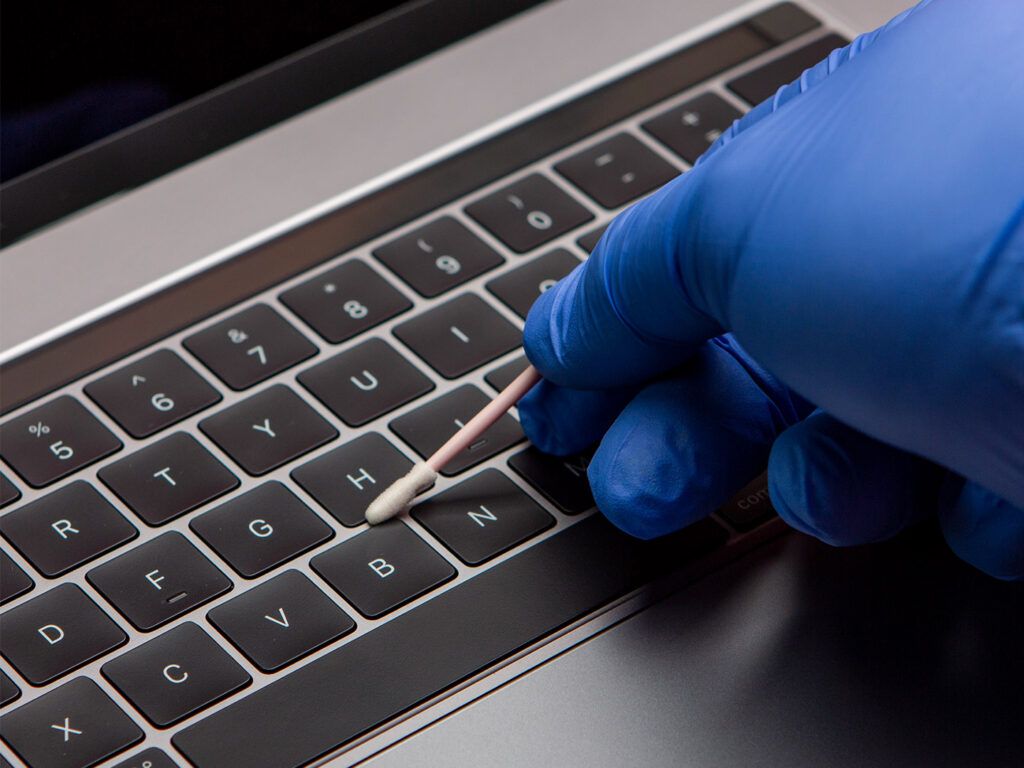
Application: ESD swabs are used for cleaning and applying solutions in cleanrooms and other critical environments where static electricity can potentially cause damage.
Usage: ESD swabs are used for various purposes, including applying and removing lubricants and adhesives, cleaning recessed areas, and scrubbing intersecting surfaces and joints.
Advantages: These swabs prevent static buildup and electron transfer, which can harm sensitive materials. They are packaged in anti-static bags and often lot-coded for traceability or quality control.
To reduce the risks associated with electrostatic discharge (ESD), it is essential to use anti-static materials such as ESD swabs, implement proper handling procedures, and maintain controlled environments when manufacturing, assembling, and maintaining electronic devices. Understanding ESD and using the proper swabs is vital for protecting sensitive electronics and ensuring reliable application performance.





























HAVE AN IDEA FOR CONTENT?
We are always looking for ideas and topics to write about.
Contact Us